Symptoms of lung cancer at an early stage. What are the different stages of lung cancer?
All diseases that are known to modern science today have certain symptoms and signs. Some diseases are similar in their external manifestations, some are different. Lung cancer in this case is no exception. Knowing the signs and symptoms of lung cancer is very important for a timely and correct diagnosis and choice of further treatment. Why is it so necessary? The fact is that only in the early stages of cancer is curable. In our article, we will try to talk about all the symptoms and signs of this disease. But I want to immediately warn you, this information is given for informational purposes only. To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, an examination by a specialist is necessary!
What is the difference between symptom and sign? Classification of lung cancer
In order to move on to a conversation about what signs and symptoms of lung cancer can be observed in a patient, it is necessary to define these terms and introduce them to the classification lung cancer(this is important because each type of lung cancer has its own symptoms and signs). Signs of a disease are objective evidence of a disease in a particular person. Signs can be detected both by the patient himself and by an outsider (doctor, relatives). Symptoms of a disease are any subjective sign of an illness. In other words, it is the feeling experienced by the patient.
Classification of lung cancer:
- By morphology:
❋ small cell;
❋ squamous;
❋ adenocarcinoma or glandular cancer;
❋ large cell;
❋mixed. - By location:
❋ central;
❋ peripheral.
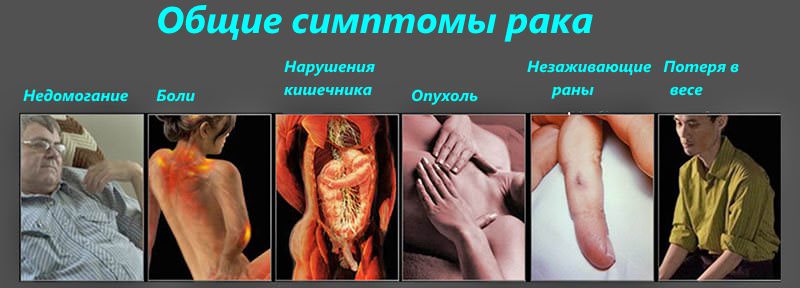
What are the symptoms of lung cancer?
Symptoms of lung cancer at different stages have significant differences. In the first stages of lung cancer (for any of its types), a person usually feels lethargic, his working capacity decreases, fatigue increases, interest in all the events of his life and society disappears. In the later stages, symptoms inherent in lung cancer are added.
small cell cancer
With small cell lung cancer, a certain group of symptoms is observed. A person begins to suffer from a cough, the attacks of which cannot be suppressed in any way. Also, when sputum is separated, blood streaks and clots can be seen in it (this is due to the fact that the bronchial wall is disturbed. Its mucous membrane and the capillaries in it are destroyed). Usually, noticing this symptom in themselves, people immediately turn to the doctor. This symptom usually indicates that the cancer is coming in stages 3 or 4.
Also characteristic of small cell carcinoma:
- pain in the chest area;
- shortness of breath;
- loss of appetite;
- body weight loss;
- increasing weakness throughout the body.
Pain in the chest area most often occurs from the diseased lung. They can vary in strength. When the tumor affects the thoracic fascia, intercostal nerves and ribs, the pain can become unbearable, constant and in many cases not amenable to pain relief with analgesics.
Shortness of breath in lung cancer is observed in case of violations in the work of some parts of the lung and squeezing of the organs that form the mediastinum (heart, aorta, arteries, veins, trachea, esophagus). Such symptoms are typical for cancer in an advanced stage.
Sometimes with this type of cancer, obstructive pneumonia (which develops against the background of bronchial obstruction or blockage), pleurisy and loss of airiness of one of the parts of the lung can manifest itself. At the 3rd and 4th stages of cancer, due to the tumor affecting the mediastinal organs, dysphagia develops (disturbances in the act of swallowing), hoarseness in the voice (due to a violation of the innervation of the area by the laryngeal nerve), and compression of the superior vena cava.
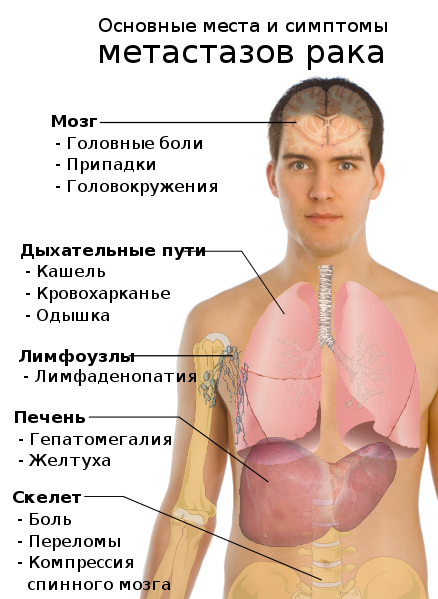
Small cell carcinoma is characterized by the rapid formation of metastases in the lymph nodes, adrenal glands, liver, bones and brain.
In this case, the symptoms of lung cancer will depend on the location of the metastases. The patient may have:
- pain in the spinal column;
- jaundice;
- headache;
- periodic dizziness and loss of consciousness.

Squamous cell carcinoma
At stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma occurs with virtually no symptoms. That is why it is first detected only during a fluorographic examination (which must be done annually).
Symptoms of this type of cancer are: primary (local) and secondary (that is, due to the formation of metastases and complications). Local symptoms appear early and arise due to the growth of the primary tumor. These include:
- cough (first dry);
- hemoptysis (at stage 4, it can even develop into pulmonary bleeding);
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath.
Over time, lung cancer progresses and secondary symptoms appear. They may be related to:
- inflammatory processes occurring in the patient's body;
- germination of tumor tissue in neighboring organs and vessels;
- with compression of internal organs;
- metastasis;
- the general effect on the body of the waste products of a malignant formation.
Often, against the background of cancer, pneumonia develops, which is accompanied by fever and a wet cough with purulent sputum. With the germination of the tumor nearby organs, the patient notes:
- dysphagia;
- hoarseness in the voice;
- severe pain in the neck and shoulder area;
- violations of the purity of the heartbeat.
Common symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- weakness, drowsiness;
- apathy for life;
- sharp weight loss;
- in severe cases - extreme exhaustion of the body (cachexia).
Adenocarcinoma or glandular cancer
Manifestations of adenocarcinoma initial stage similar to the symptoms of other types of cancer (fatigue, blood disorders, apathy, and so on). They are invisible and for a long time the patient is not even aware of a malfunction in his body. Over time, cancer cells begin to grow actively and a person begins to suffer from:
- cough of unknown etiology (in the later stages with bloody sputum);
- changes in the pitch of the voice, its melody and timbre;
- hoarseness (due to the effect of cancer cells on the vocal cords and larynx);
- shortness of breath (during exercise, walking, and in the last stages even at rest);
- pain in the chest;
- frequent inflammation of the lungs and their serous membrane (pleura).
Also, with this type of lung cancer, it is noted:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- temperature, which for a long time keeps at around 37.1-38.
Large cell cancer
With the development of a large cell lung cancer, the patient shows similar symptoms with other types of cancer. At stages 1 and 2, the symptoms are non-specific (that is, inherent in other disease states), in some cases they may be completely absent.
At stages 3 and 4 begins:
- cough that can't be stopped medicines. At first it is predominantly dry, hoarse. In the process of growth of tumor cells, it becomes wet (with sputum in which bloody streaks are found);
- pneumonia, which is treated with great difficulty;
- radiating to the heart muscle, back, arms pain in the chest;
- voice hoarseness, and at an advanced stage of the disease, even aphonia (in case of damage to the larynx and vocal cords);
- shortness of breath due to deterioration in the plasticity of lung tissue;
- pain in other organs (due to extensive metastasis).
mixed cancer
Mixed lung cancer is a combination of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Or adenocarcinoma and small cell lung cancer. Therefore, his symptoms will be similar to these types of cancer.
Central cancer
Symptoms of lung cancer, like any other disease, depend more on the location of the tumor than on its histology. The diagnosis of "central lung cancer" means by itself - the defeat of cancer cells in the mucous membrane of the lung. Gradually growing, the tumor causes pain, disorders of the innervation of the organ and damage to the lining of the lung - the pleura.
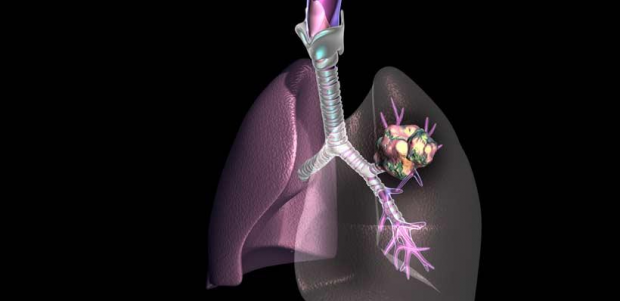
Due to local metastasis, symptoms may appear, which can be found below:
- When the tumor grows into the bronchi:
❋ dry cough, which, with the development of cancer, becomes purulent and acquires an unpleasant odor;
❋ high temperature;
❋ weakness in the body;
❋ breathing difficulties;
❋ Cancerous pleurisy and pneumonia are possible. - For vagus nerve injury:
❋ changes in voice (hoarseness, hoarseness, etc.);
❋ paralysis of the vocal folds. - With the germination of the central tumor in the shell of the heart - the pericardium:
❋ pain in the area where the heart is located. - In the superior vena cava:
❋ violations in the supply of blood and lymph to the chest, arms and neck.
peripheral cancer
Since lung tissues do not have any pain endings, the initial stage peripheral tumor in the lungs has no symptoms. Over time, the tumor begins to grow rapidly and damages the bronchi, pleura and neighboring organs. Often this process is accompanied by bleeding.
The development of peripheral cancer also causes:
- causeless prolonged cough with bloody sputum;
- hoarseness of voice;
- compression of the superior vena cava (SVC) if the cancer has invaded the apex of the lung;
- pain due to damage to nearby organs to the lung;
- cancerous pleurisy;
- Pancoast syndrome (pain in the shoulder area, destruction or destruction of part of the upper ribs, lack of sensitivity of the hands, muscle weakness in them, and in severe cases, atrophy).
Common symptoms in peripheral lung cancer include shortness of breath (due to metastasis of the tumor to the lymph nodes), weakness, sudden weight loss due to impaired appetite, and fever.

Signs of lung cancer
Signs characteristic of lung cancer as well as the disorders that it causes are quite diverse. First of all, they depend on the stage in which the disease is located. One of the most typical signs is the absence of any health complaints in the patient at the first stage of the disease. This is due to the fact that the cancer grows for quite a long time (sometimes several years).
In the process of development, a cancerous tumor goes through 3 stages:
- biological (from the appearance of cancer cells to the moment when it can be seen during x-ray examination);
- preclinical (the presence of the disease is shown only by an x-ray. This period is also called asymptomatic);
- clinical (the first characteristic symptoms disease).
Cancer stage 1 and 2 is in the biological or preclinical period of its development. Such cancer can only be detected by chance (because there are no ailments, there are no symptoms and signs of a tumor in the lungs, and a person does not even suspect that he has such a serious illness). As statistics show, patients in most percent of cases seek medical help only when signs of illness and indisposition appear, that is, at stages 3 or 4. But even during this period, the signs of the disease are quite non-specific (that is, inherent in other diseases respiratory system).
It's connected with:
- the effect of products of tumor activity on the human body;
- changes in the lymphatic trunks and ducts;
- inflammatory or purulent-destructive changes in the tissues of the lung or pleura;
- metastasis to other organs.
Carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm that affects the tissues of various organs and systems. Initially, a cancerous tumor forms from the epithelium, but then quickly grows into nearby membranes.
lung carcinoma - oncological disease in which the tumor is formed from the cells of the bronchial mucosa, alveoli or bronchial glands. Depending on the origin, two main types of neoplasms are distinguished: pneumogenic and bronchogenic cancer. Due to the rather erased course at the initial stages of development, lung oncology is characterized by late diagnosis and, as a result, a high percentage of deaths, reaching 65-75% of the total number of patients.
Attention! Modern methods therapy can successfully cure lung cancer at stages I-III of the disease. For this, cytostatics, radiation exposure, cytokine therapy and other medical and instrumental techniques are used.
At the same time, it is also necessary to distinguish cancerous tumors from benign ones. Often the need to differential diagnosis pathology leads to a delay in making an accurate diagnosis.
Characteristics of neoplasms
| Benign neoplasms | carcinomas |
|---|---|
| The cells of the neoplasm correspond to the tissues from which the tumor was formed. | Carcinoma cells are atypical |
| Growth is slow, the neoplasm grows evenly | Infiltrating rapid growth |
| Does not form metastases | Intensively metastasize |
| Rarely recur | prone to relapse |
| Virtually no detrimental effect on the general well-being of the patient | Lead to intoxication and exhaustion |
The symptoms of this disease can vary greatly. It depends both on the stage of tumor development, and on its origin and localization. There are several types of lung cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma is characterized by slow development and relatively non-aggressive course. Undifferentiated squamous cell carcinoma develops faster and gives large metastases. The most malignant is small cell carcinoma. Its main danger is an erased current and rapid growth. This form of oncology has the most unfavorable prognosis.
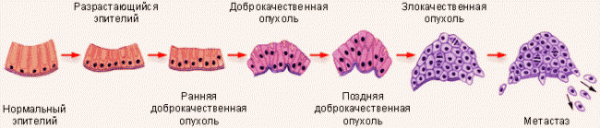
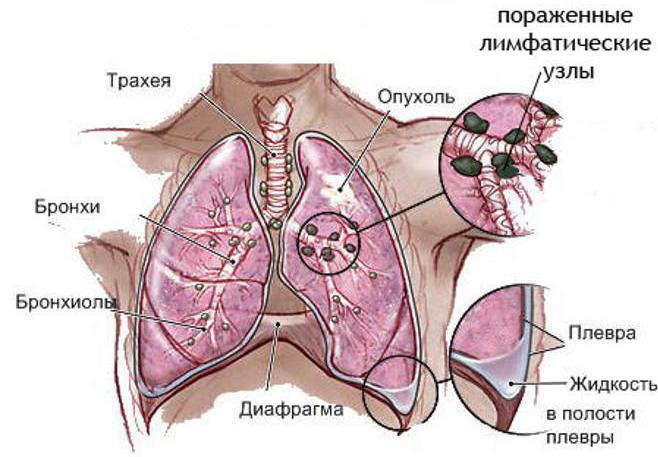
Unlike tuberculosis, which most often affects the lower lobes of the lungs, cancer in 65% of cases is localized in the upper respiratory tract. Only in 25% and 10%, carcinoma is detected in the lower and middle segments. Such an arrangement of neoplasms in this case is explained by active air exchange in the upper lobes of the lungs and the deposition on the alveolar tissue of various carcinogenic particles, dust, chemicals, etc.
Lung carcinomas are classified depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease and distribution. There are three main phases in the development of pathology:
- biological phase. It includes the moment from the onset of tumor formation to the appearance of its first signs on a tomogram or radiograph.
- Asymptomatic phase. At this stage, the neoplasm can be detected using instrumental diagnostics, but the patient does not yet show clinical symptoms.
- The clinical phase, during which the patient begins to worry about the first signs of pathology.
Attention! During the first two stages of tumor formation, the patient does not complain about a violation of well-being. During this period, it is possible to establish the diagnosis only during a preventive examination.
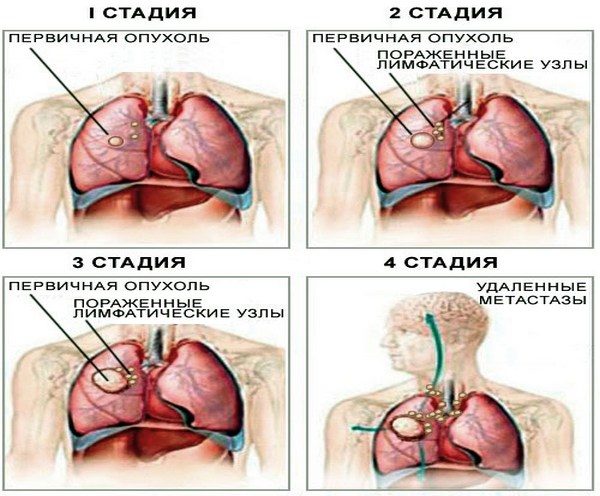
It is also necessary to distinguish four main stages in the development of the oncological process in the lungs:
- Stage I: a single neoplasm does not exceed 30 mm in diameter, there are no metastases, the patient may be disturbed only by a rare cough.
- Stage II: the neoplasm reaches 60 mm, can metastasize in the next The lymph nodes. The patient at the same time complains of discomfort in the chest, slight shortness of breath, cough. In some cases, low-grade fever is noted due to inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Stage III: the diameter of the neoplasm exceeds 60 mm, while the germination of the tumor into the lumen of the main bronchus is possible. The patient experiences shortness of breath on exertion, chest pain, cough with bloody sputum.
- Stage IV: carcinoma grows beyond the affected lung, various organs and distant lymph nodes are involved in the pathological process.
The first symptoms of lung carcinoma
For some period of time, the pathology develops hidden. The patient does not experience any specific symptoms suggestive of a lung tumor. The development of carcinoma can proceed many times faster if there are some provoking factors:
- living in ecologically unfavorable areas;
- work in hazardous industries;
- chemical vapor poisoning;
- smoking;
- genetic predisposition;
- transferred viral and bacterial infections.
Initially, the pathology manifests itself as an inflammatory disease of the respiratory system. In most cases, the patient is misdiagnosed with bronchitis. The patient complains of recurrent dry cough. Also, people in the early stages of lung cancer have the following symptoms:
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- loss of appetite;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- slight hyperthermia up to 37.2-37.5;
- hyperhidrosis;
- decreased performance, emotional instability;
- bad breath on exhalation.
Attention! The lung tissue itself does not have sensitive endings. Therefore, with the development of oncological disease, the patient may not experience pain for a sufficiently long period.

Symptoms of lung carcinoma
In the early stages, it is often possible to stop the spread of the tumor by radical resection. However, due to the blurring of symptoms, it is possible to identify pathology at stages I-II in a rather small percentage of cases.
The pronounced characteristic clinical manifestations of the pathology can usually be fixed when the process passes to the stage of metastasis. Manifestations of pathology can be varied and depend on three main factors:
- clinical and anatomical form of carcinoma;
- the presence of metastases in distant organs and lymph nodes;
- disturbances in the functioning of the body caused by paraneoplastic syndromes.
AT pathological anatomy Tumor processes of the lungs are divided into two types of tumors: central and peripheral. Each of them has specific symptoms.
Central carcinoma is characterized by:
- wet debilitating cough;
- sputum discharge with blood inclusions;
- severe shortness of breath;
- hyperthermia, fever and chills.
With peripheral oncology, the patient has:
- soreness in the chest;
- dry unproductive cough;
- shortness of breath and wheezing in the chest;
- acute intoxication in case of decay of carcinoma.
Attention! In the initial stages of the pathology, the symptoms of peripheral and central lung cancer differ, but as the oncology progresses, the manifestations of the disease become more and more similar.
Most early symptom with lung carcinoma - cough. It occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings of the bronchi and the formation of excess sputum. Initially, patients have a dry cough that worsens with exertion. As the neoplasm grows, sputum appears, which is first mucous, and then purulent and bloody.
Shortness of breath occurs at a fairly early stage and appears due to excess mucus in the airways. For the same reason, patients develop stridor - strained wheezing. Percussion heard moist rales and squelching in the lungs. As the tumor grows, if it blocks the lumen of the bronchus, shortness of breath is noted even at rest and rapidly intensifies.
Pain syndrome occurs in the late stages of oncology with the germination of carcinoma in the tissues of the bronchial tree or surrounding tissues of the lungs. Also, discomfort during respiratory movements can disturb the patient due to the addition of secondary infections to the disease.
Gradually, the growth of the tumor and the spread of metastases provoke compression of the esophagus, violation of the integrity of the tissue of the ribs, vertebrae and sternum. In this case, the patient has pain in the chest and back, which is of a constant dull character. Difficulties in swallowing are noted, a burning sensation in the esophagus is possible.
Oncology of the lungs is most dangerous because of the rapid growth of metastases in large vessels and the heart. This pathology leads to angina attacks, intense cardiac dyspnea, impaired blood flow in the body. During examination, the patient has arrhythmia, tachycardia, ischemic zones are revealed.
Paraneoplastic syndromes
Paraneoplastic syndrome is a manifestation of the pathological effects of a malignant neoplasm on the body. It develops as a result of tumor growth and is manifested by various non-specific reactions from organs and systems.
Attention! In most cases, such manifestations of the disease occur in patients at stages III-IV of carcinoma development. However, in children, the elderly, and patients with poor health, paraneoplastic syndrome can also occur at earlier stages of tumor formation.

Systemic syndromes
Systemic paraneoplastic syndromes are manifested by a large-scale lesion of the body, in which various organs and systems are affected. The most common symptoms of lung cancer are:
Attention! Systemic syndromes must be carefully and urgently stopped. Otherwise, they can dramatically worsen the patient's condition and lead to his death.
Video - Lung cancer: the first symptoms
Skin syndromes
Skin lesions develop for several reasons. The most common factor provoking the appearance of various pathologies of the epidermis is the toxic effect on the human body of a malignant neoplasm and cytostatic drugs. All this weakens the protective functions of the body and allows various fungi, bacteria and viruses to infect the skin and epithelial integuments of the patient.
In patients with lung carcinoma, the following syndromes are noted:
- hypertrichosis - excessive hair growth throughout the body;
- dermatomyositis - an inflammatory pathology of the connective tissue;
- acanthosis - coarsening of the skin at the site of the lesion;
- hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy - a lesion that leads to deformation of bones and joints;
- vasculitis is a secondary inflammation of blood vessels.
Hematological syndromes
Circulatory disorders in patients with oncological diseases develop quite quickly and can manifest themselves already at stages I-II of the pathology. This is caused by a sharp negative impact of carcinoma on the functioning of the hematopoietic organs and a violation of the full functioning of the lungs, which causes oxygen starvation of all systems of the human body. Patients with lung cancer show a number of pathological symptoms:
- thrombocytopenic purpura - increased bleeding, leading to the appearance of hemorrhages under the skin;
- anemia;
- amyloidosis - a violation of protein metabolism;
- hypercoagulability - an increase in the coagulation function of the blood;
- leukemoid reaction - various changes in the leukocyte formula.
Neurological syndromes
Neurological paraneoplastic syndromes develop in connection with damage to the central or peripheral nervous system. They arise due to a violation of trophism or in connection with the germination of metastases in the spinal cord or brain, which is quite often observed in lung carcinomatosis. Patients have the following disorders:
- peripheral neuropathy - damage to peripheral nerves, leading to impaired mobility;
- myasthenic Lampert-Eaton syndrome - muscle weakness and atrophy;
- necrotizing myelopathy - necrosis of the spinal cord, leading to paralysis;
- cerebral encephalopathy - brain damage;
- vision loss.

Symptoms of stage IV oncology
AT rare cases patients seek medical help only at the stage when oncology turns into carcinomatosis, and the pain becomes unbearable. Symptoms at this stage largely depend on the spread of metastases throughout the body. To date, stage IV lung cancer is extremely difficult to treat, so it is necessary to consult a specialist when the first warning signs appear.
Attention! Carcinomatosis is a multiple metastasis in cancer. With carcinomatosis, any system or the entire body of the patient can be completely affected.
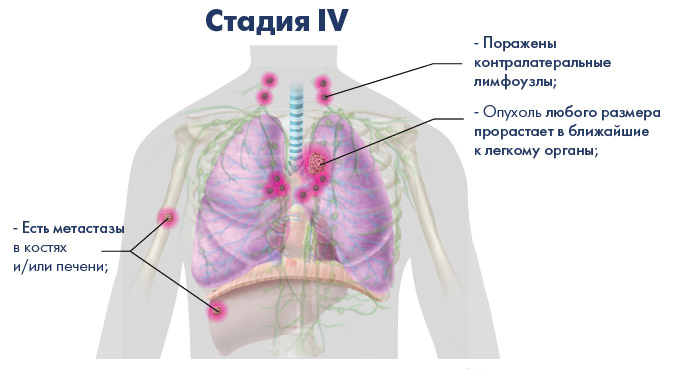
A patient in the late stages of tumor formation develops the following symptoms, indicating a violation of the work of various organs and systems:
- debilitating long-lasting coughing fits;
- sputum with blood, pus and decay products of the lungs;
- apathy, depression;
- constant drowsiness, impaired cognitive function;
- cachexia, weight loss to critical levels: 30-50 kg;
- swallowing disorder, vomiting;
- painful attacks of cephalalgia;
- profuse pulmonary bleeding;
- delirium, impaired consciousness;
- intense persistent pain in the area chest;
- respiratory failure, suffocation;
- arrhythmia, violation of the frequency and filling of the pulse.
Oncological lung disease appear alongside various symptoms. The most characteristic alarming signals of pathology are a long-lasting cough with sputum, chest pain and wheezing when breathing. When such signs appear, it is necessary to consult a pulmonologist for advice.
Video - Lung Cancer: Causes and Symptoms
This type of tumor is the most common among cancers. Previously, he belonged only to the male sex, but recently the disease has become common among women. Signs of lung cancer are diagnosed in every 10th cancer patient. It is a disease of a malignant epithelial tumor with the possibility of spreading metastases. The main difficulty is that at an early stage, lung cancer is almost asymptomatic, and a person turns to a doctor too late.
The main symptoms and signs of lung cancer in women and men
Depending on the type of cells from which the tumor was formed, small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer are isolated. Symptoms among men and women are similar, there are no cardinal differences. As a rule, with the development of a tumor for a long time, no alarming, unpleasant signs are observed. This is a characteristic feature of long-term tumor growth. There are three phases of the development of the disease, which have the following clinical picture:
- Biological. It is determined from the moment of the onset of the tumor until the manifestation of radiological signs.
- Asymptomatic (preclinical). There are radiological signs.
- Clinical. In addition to X-ray, clinical symptoms are observed.
- The tumor is located in one place, does not metastasize, the diameter of the formation is not more than 4 cm. External and radiological symptoms in this phase are absent or appear so slightly that the person does not attach importance to them. In this phase, the cough is disturbing, headache, general malaise, loss of appetite, fever. It is impossible to diagnose lung cancer by these symptoms, based on the patient's complaints. To do this, you should do an MRI or fluorography.
- The second stage may have primary metastases in the lymph nodes, the size of the neoplasm grows. The symptoms are still blurred, but already more noticeable, which should alert the patient and the doctor. During this period, hemoptysis, chest pain, wheezing during breathing, along with the above symptoms, may begin.
- In the third stage, cancer can be diagnosed based on the patient's complaints and medical examination. Confirmation is the presence of metastases in all regional lymph nodes, some distant ones. The tumor grows so much that it extends beyond the lung. The symptoms are the same as in the second stage, but with a higher intensity. noted wet cough with mucus, sometimes with blood and pus, breathing is difficult, shortness of breath, sore throat when swallowing.
- In the fourth stage, there is a severe course of the disease with vivid symptoms. The cough becomes constant, disturbing and hacking, regular hemoptysis, fluid accumulates in the lung with cancer, chest pain of varying intensity. In addition to the respiratory system, symptoms of lung cancer include cardiovascular and digestive symptoms. This is due to the increase, growth of the tumor.
What are the early signs
For successful treatment, it is important to identify the first symptoms at an early stage. The difficulty is that the manifestations are nonspecific, they can be confused with many other diseases: this causes an untimely visit to the hospital. In the presence of such symptoms, it is necessary to pay attention to your condition and go to the doctor. List of primary clear signs of lung cancer:
- cough;
- chest pain;
- weight loss;
- temperature rise;
- dyspnea;
- hemoptysis.
Temperature in oncology
One of the symptoms of lung cancer is fever. The problem with this symptom is its non-specificity; many other diseases have the same manifestation. Regularity should be an important manifestation for you. high temperature(38°C) for a long time. Most people with this symptom simply take antipyretics and for a short time they really help. The temperature returns in 2-3 days to the previous values.

What is a cough for lung cancer
A typical symptom of lung cancer is a cough. This is a protective reaction of the body to irritation of specific receptors. Occurs with prolonged internal or external exposure to them. For different stages of a lung tumor, a different type of cough is characteristic. This is one of the first signs of the development of the disease, which is rarely paid attention to. Cough with cancer can be of the following nature:
- Short cough. It has a special timbre and is characterized by a strong, rapid contraction of the abdominal muscles. For lung cancer, a regular and frequent cough of this type is typical.
- Coughing. Has a convulsive and permanent character. Attacks often occur before sleep, resemble convulsions of the respiratory tract, in the worst case, accompanied by vomiting. Sometimes, due to such a cough, the heart rhythm can be disturbed, fainting or loss of consciousness can occur.
- Dry cough. In the case of lung cancer, it has an hysterical character, as a rule, slightly muffled, hoarse, sometimes silent and without sputum.
Hemoptysis
In the later stages of the disease, the symptoms become more specific. It is worth noting that this manifestation may be a sign of tuberculosis or simply a rupture of a blood vessel. Hemoptysis in lung cancer appears in the second stage of the disease. Outwardly, the blood may be in the form of streaks in the sputum or clots. In the worst case, pulmonary hemorrhage may begin during the collapse of the tumor, when the patient coughs up blood with a full mouth, chokes on it. If there are blood clots or streaks in the sputum, you should consult a doctor.
Sputum
A typical manifestation of lung cancer is expectoration of sputum when coughing. Visually, it is light, mucous, sometimes with streaks of blood, which should immediately alert a person and make him see a doctor. Blood in the sputum becomes a serious reason for bronchoscopy, a photo of the chest using an x-ray. With a bronchoalveolar form of cancer, up to 200 ml of foamy sputum per day is possible. In the later stages and advanced stages of cancer, sputum may become mucopurulent, with the decay of the tumor it has a crimson color, and resembles jelly in structure.
How do lungs hurt with cancer?
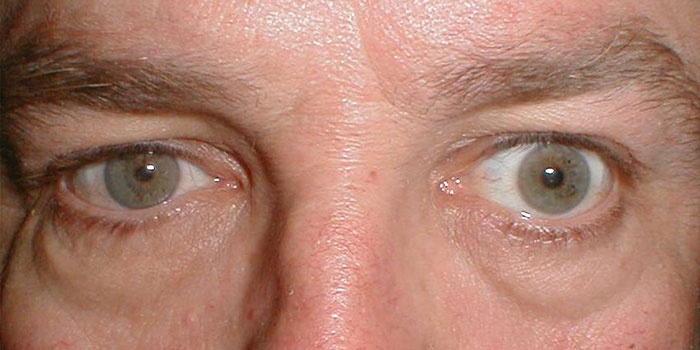
In most cases, lung cancer pain occurs on the affected side. The nature of this disease can be different in intensity. This is due to the participation in the process of the parietal pleura, and later - the intrathoracic fascia, ribs and intercostal nerves. The last manifestation creates especially strong pain sensations, they are painful, permanent. The transition of the tumor from the apex of the lung to the brachial plexus is possible, which leads to the manifestation of Horner's syndrome. The nature of the pain can be:
- stabbing;
- acute;
- encircling;
External signs
- The face becomes dull, pale, gray. Possible yellowish color of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Metastases in lung cancer cause inflammation of the lymph nodes in the subclavian and axillary region.
- The neck, face and upper half of the body becomes edematous.
- The collateral veins on the chest are dilated.
- Horner's syndrome is an unusual symptom.

Causes of cancer
The lungs are the only internal organ that has direct contact with the external environment. Everything that a person inhales almost unchanged reaches the alveoli, because of this, the cells of the mucous membranes of the bronchi have an increased rate of renewal. Dust, smoke or fog contains organic and inorganic aggressive substances that adversely affect the microvilli of the epithelium. This becomes the main risk factor for the development of neoplasms in the lungs. The main causes of lung tumor development:
- Smoking. Most high risk when using cigarettes (25 times compared to non-smokers), but a pipe and a cigar cause swelling less often (5 times).
- Second hand smoke. The method of penetration of smoke with aggressive substances is not important. Even just being close to a smoker can result in the development of a tumor.
- asbestos fibers. Silicone fibers of this substance can stay in the lungs for a long time, provoking the development of cancer. Workers in the asbestos industry have a 5 times higher incidence of the disease than non-smokers in other industries.
- Radon gas. This substance is a decomposition product of uranium and can provoke the development of lung cancer.
- hereditary predisposition. If you have relatives with this disease, the risk of developing it increases, even if you do not smoke.
- Other diseases. In the presence of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), the possibility of cancer is increased by 4-6 times.
Survival and life expectancy
Lung cancer is a disease a high degree mortality, which is associated with the indispensability of the respiratory function and its importance. According to statistics, adult smokers are most susceptible to developing a tumor. At different stages of the disease, there is a possibility of five-year survival. The indicator is higher for those who receive medical care with early detection of neoplasm. An individual prognosis is given to each person based on complete information about the course and stage of the disease. How long a person will live also depends on the location of the outbreak.
- People with peripheral lung disease have a high chance. Cases have been recorded when death occurs 10 years after diagnosis. In this case, even at the 4th stage, patients do not feel strong pain symptoms.
- Low chances in people with central cancer. A person dies within 3-4 years. The tumor behaves aggressively in the last stages and even the most effective treatment does not give the desired result.
Video about the signs of a tumor and cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. Most often men suffer from it. In this case, about 70% of cases end in death. In order to protect yourself from such an ailment, you need to know the causes of its occurrence.
The main causes and pathogens of lung cancer
Lung cancer is often associated with smoking. Indeed, about 65% of the patients abused cigarettes. Inhalation of tobacco smoke can be called the main cause of lung cancer. But cancer is also common in non-smokers. In this case, the causes of the disease may be as follows:
These symptoms are equally true for both men and women. It is worth remembering that the female body is more vulnerable, its health must be monitored carefully.
Scientists around the world are trying to find a reliable answer to the question of what causes lung cancer. But in many cases, the etiology of the disease remains uncertain.
Experts have identified a number of substances, after contact with which, oncology may appear. Among them are:

Each of these substances can accumulate in the lungs of a person and have a toxic effect. Over time, they corrode the mucous membranes, and provoke the degeneration of healthy cells into cancerous ones.
Pathogenesis
Due to the intensive division of cancer cells, the size of the tumor increases quite quickly. If the problem is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started, then the cardiovascular system, esophagus and spine are affected.
The mutated cells enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. The process of dividing cancer cells does not stop.
This leads to the formation of metastases in the liver, lymph nodes, bones, kidneys and brain. Based on the histological structure, lung cancer can be divided into 4 large subgroups:
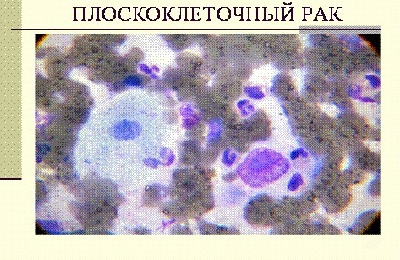
The pathogenesis of lung cancer largely depends on cell differentiation. The lower it is, the more dangerous the tumor.
Lung cancer appears as a result of mutation of epithelial cells. The incidence of tumors in the left and right lung is approximately the same. Depending on the location, the following types of cancer are distinguished:

In order to slow down the development of the tumor, it is necessary to exclude the influence of risk factors for lung cancer.
Psychosomatic causes of the development of the disease
The development of a malignant tumor is often associated with a complex psychological state of a person. malignant neoplasm- this is a mutation of healthy cells, the appearance of an internal enemy in the body. He becomes one with the patient.
 Experts attribute a person's poor psychological state to risk factors for developing lung cancer. The most dangerous of all negative emotions are resentment, guilt and deep disappointment. The cause of the disease can also be a severe moral shock, the loss of a loved one.
Experts attribute a person's poor psychological state to risk factors for developing lung cancer. The most dangerous of all negative emotions are resentment, guilt and deep disappointment. The cause of the disease can also be a severe moral shock, the loss of a loved one.
It is believed that time can heal. But in fact, the pain does not disappear anywhere, it just clogs deeper and becomes invisible outwardly. Gradually, it thickens, and lies on the soul of a person like a heavy stone. If the patient fails to find a way to get rid of this stone, then it can develop into malignant tumor.
Experienced negativity deprives a person of the desire for a happy life. He is overcome by a constant feeling of hopelessness and fear. These emotions disrupt the hormonal and immune system organism. Because of this, the body simply no longer has the strength to resist cell mutation.
Working with cancer patients, psychologists try to learn more about their biography. The fact that the tumor began to develop in the lungs speaks of a heavy sense of resentment.
Only by finding out the root cause of the problem, understanding it, can the patient's condition be alleviated. If an oncological disease struck a child, then the reason should be looked for in the worldview and psychological state of the parents. The child's psyche is not yet fully formed. At a young age, we are very receptive and adopt everything. negative emotions from the people around us.
Lung cancer can be triggered by a person's disappointment in their life. Gradually, his interest in everything that happens around fades away. He becomes indifferent to others, his own health and life.
An Eastern woman is diagnosed with lung cancer in an inoperable stage. Doctors cannot identify a significant factor that caused the disease. After studying her biography, it becomes clear that the tumor was caused by resentment that had accumulated in a woman all her life.
In early childhood, she was abandoned by her father under bad circumstances. Since it took place in an eastern country, the family was branded with shame. As he grew older, resentment against his father only accumulated. The woman became hard and cold. The family, created by herself, outwardly seemed prosperous, but there was no kindness in it. These circumstances led to the development of oncology.
It is important not only to monitor the health of your body, but also to be able to create harmony of the soul. Learn to forgive insults, do not lose interest in life, try to do good. Then your body will not allow the cells to mutate.
Clinical picture
In order to defeat cancer, it must be diagnosed on time. In the early stages, the disease is treatable. Therefore, you need to carefully monitor your health and remember a few symptoms of oncology that you can identify yourself:

If you notice these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Early stages of cancer are difficult to determine by outward signs. A medical examination will be required. During the study, the doctor reveals the following signs of the disease:

Upon detection similar symptoms additional examination will be required. In some cases, a biopsy is ordered.
This is a puncture of the chest and sampling of a part of the neoplasm. Such a study allows us to speak with confidence about the nature of the tumor. Only a comprehensive examination of the patient will allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and develop the correct treatment program.
Preventive actions
In order to less often think about lung cancer and the causes of its occurrence, you need to carefully monitor your health. You must adhere to the following recommendations:

Such simple tips will help you protect yourself not only from cancer, but also from other diseases of the respiratory system. You need to take good care of your health. Any worrisome symptoms should be treated by a specialist.
Lungs' cancer is a malignant tumor that develops from the mucous membrane and glands of the bronchi and lung tissue. The main reason for the development of lung cancer is smoking.
Types of lung cancer
Based on what type of cells the tumor consists of, Lung cancer is divided into two main types:small cell - the most aggressive type of cancer that can quickly spread throughout the body and give tumors in other organs - metastases. This type of lung cancer It is rare and is typical, as a rule, for smokers.
non-small cell lung cancer occurs in a higher percentage of cases. Its development is quite slow.
There are three types of such development: squamous cell lung cancer (comes from squamous cells, is characterized by slow growth), adenocarcinoma (a tumor that develops from cells that produce mucus) and large cell carcinoma.
Based on where the tumor is located, lung cancer is classified into into central and peripheral. Lung cancer central type located in the large bronchi, its characteristic symptoms appear earlier. Peripheral lung cancer is localized on the periphery of the lungs - in the small bronchi, proceeds for a long time without pronounced symptoms and is usually detected during preventive fluorography.
Causes of lung cancer
The main factors that contribute to the development of lung cancer are as follows:1. Nicotine addiction is main reason occurrence of lung cancer. The risk of developing lung cancer in a smoker depends on age, the number of cigarettes smoked per day, and also on how long a person smokes. If you completely stop smoking, the risk of lung cancer gradually decreases, but it will never again reach the initial level. Because nicotine addiction is not the only risk factor for lung cancer, non-smokers do not exclude the risk of developing this disease.
There are more than four thousand varieties of cancer-causing poisonous carcinogens that are released when tobacco is burned. The most famous and most dangerous of them are: toluidine, benzpyrene, heavy metals (polonium, nickel), naphthalamine, nitroso compounds.
The above compounds, after entering the lungs with inhaled cigarette smoke, settle on the delicate mucous membrane of the bronchi. At the same time, they, as it were, burn it out, destroy living cells, lead to the death of the ciliated epithelium - the mucous layer, penetrate through blood vessels into the blood and spread throughout the body, getting into the internal organs, kidneys, liver, brain, leading to similar changes in them.
All the harmful compounds that we breathe in cigarette smoke stay in the lungs forever.
They cannot be absorbed and excreted, while they form clusters, as a result, the lungs are slowly covered with black soot. At healthy person the lungs have a soft porous structure, a pale pink color, the lungs of a smoker are a rough, inelastic tissue that has acquired a blue-black or black color.
2. In the development of lung cancer also plays a role genetic predisposition. Scientists have discovered a gene whose presence significantly increases the risk of lung cancer, even if a person does not smoke. Hence the conclusion that relatives of patients with lung cancer are at higher risk of developing this type of cancer.
3. Greater risk of lung cancer environmental factors: exhaust fumes, significant dust content in the air in urban industrial areas, passive smoking - a frequent presence among people suffering from nicotine addiction for a long time, radiation, factors associated with professional activities ( prolonged contact with asbestos, nickel, arsenic, chromium, work in coal mines, etc.).
4. chronic diseases lung, such as, for example, COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or tuberculosis, lead to an increased risk of developing lung cancer.
Signs and symptoms of lung cancer
Lung cancer manifests itself depending on what type it belongs to, on the location, stage of the disease and the degree of spread. There are such main symptoms characteristic of lung cancer:1. The most common symptom of lung cancer is a prolonged cough. With lung cancer, the cough is usually persistent, dry (without sputum), but at the same time, it can produce mucopurulent sputum or hemoptysis - sputum secretion containing scarlet streaks of fresh blood.
2. With lung cancer, there is a feeling of lack of air during physical activity or at rest (so-called shortness of breath). Its appearance is due to the fact that the tumor closes the passage of air through the large bronchi, as a result of which the work of the lung area is disrupted.
3. An increase in body temperature or frequent inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia), which are especially common in a smoker, may also indicate the presence of lung cancer.
4. Pain in the chest, aggravated by taking a deep breath or coughing.
5. If the tumor grows into the large vessels of the lungs, pulmonary hemorrhages develop. Bleeding from the lungs is a dangerous complication of the course of the disease. If sputum formation is noted, in which the amount of fresh scarlet blood is increased, it is necessary to contact an ambulance as soon as possible.
6. Large lung tumors can lead to squeezing of neighboring organs and large vessels, and symptoms such as pain in the arms and shoulders, swelling of the arms and face, constant hoarseness of the voice, impaired swallowing, hiccups appear.
7. If the tumor metastasizes, i.e. spreads to other organs, a wide variety of symptoms may occur: with liver metastases - jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium; with brain metastases - lack of movement (paralysis), speech disorders, persistent loss of consciousness (coma); with bone metastases - fractures and pain in the bones, etc.
8. Cancer is characterized by some general symptoms, which cannot be explained by other reasons: weight loss, weakness, lack of appetite.
Sometimes lung cancer for a long time without symptoms and can only be detected during prophylactic fluorography.
Because most people with lung cancer are heavy smokers who have a chronic cough before the tumor develops, it can be difficult to detect early cancer based on symptoms. Therefore, if a smoker suddenly intensifies or changes in any way (accompanied by painful sensations or bloody sputum) cough, it is necessary urgently seek medical help.
Degrees (stages) of lung cancer
First stage: the size of the tumor in the lung is not more than 3 see either a bronchial tumor spreads within one lobe, metastases (metastatic tumors are screenings from the main tumor of another organ) are not produced in nearby lymph nodes;Second stage: lung tumor larger than 3 see, it blocks the bronchus, grows into the pleura, while part of the lung (atelectasis), one lobe collapses;
Third stage: the tumor spreads to neighboring structures, atelectasis of the entire lung, the presence of metastases in the nearby lymph nodes - supraclavicular, root of the lung and mediastinum;
Fourth stage: there is a germination of the tumor in the surrounding organs (large vessels, heart) or metastatic pleurisy - the addition of fluid in the pleural cavity.
Prognosis for lung cancer
In lung cancer, the prognosis depends on the stage of development of the disease and the histological structure of the lungs. Small cell carcinoma has a better prognosis than other forms of cancer because it is more sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy than other forms of the disease.The likelihood of a favorable outcome is higher if the cancer is treated in the initial stages - first and second. The prognosis for tumors of the third and fourth stages is extremely unfavorable, the survival rate for these forms of the disease does not exceed 10 %.
Diagnosis of lung cancer
All people, especially smokers, should, as far as possible, periodically screened for lung cancer. Adults undergo prophylactic fluorography (examination of the lungs by X-ray), as a rule, with a frequency of once a 12 months. If any changes are found on the fluorogram, the doctor prescribes other types of studies that will help in making the correct diagnosis.Methods used in the diagnosis of lung cancer:
1. Radiography chest. This method of diagnosing lung cancer is the most common. With the help of x-rays, the doctor examines the structure of the lungs, determines if there are suspicious blackouts, displacements of the chest organs, evaluates the size of the lymph nodes, as well as other signs that are characteristic of lung cancer. In some cases, the appearance of suspicious shadows (shadows) on the x-ray may be due to other reasons. Therefore, a method such as computed tomography is used to clarify the diagnosis.
2. CT scan is a method for diagnosing lung cancer, giving a more informative picture. With its help, you can better examine suspicious areas of the lung. In addition, computed tomography small tumors can be detected,
which are invisible on radiographs.
3. Bronchoscopy - a method for diagnosing lung cancer, in which a tumor biopsy is performed (a tumor site is taken to be examined under a microscope). During a bronchoscopy, the doctor inserts Airways a bronchoscope, which is a special flexible tube, at the end of which there is a video camera. With the help of bronchoscopy, the doctor gets the opportunity to examine the inner surface of the bronchi, if a tumor is detected, take a part of the tumor tissue for examination, i.e. perform a biopsy.
4. Needle biopsy. With the localization of a lung tumor in small bronchi, which cannot be penetrated with a bronchoscope. The biopsy is done through the skin.
5. Rarely enough, but still there are cases when it is not possible to perform a biopsy of a lung tumor using bronchoscopy or a needle. In this situation, the patient is given surgery to open the chest (thoracotomy). During the operation, the doctor determines the location of the lung tumor and takes the site in order to further examine it under a microscope.
The most reliable method for diagnosing lung cancer is tumor biopsy. If cancer cells are found in the area of the obtained material under a microscope, the diagnosis of lung cancer is confirmed. After that, the doctor prescribes additional tests that allow you to find out the stage of cancer development. Such analyzes include magnetic nuclear resonance, ultrasound examination of organs abdominal cavity and so on.
Lung Cancer Treatment
Treatment of this disease is carried out depending on the stage of development of the disease, the type of cancer (small cell or non-small cell cancer), as well as the general condition of the patient. In the treatment of lung cancer Three main methods are used which can be carried out both separately and in combination:radiotherapy,
surgery,
chemotherapy.
Lung Cancer Treatment surgical method - this is an operation performed to remove a tumor, lobe or whole lung (this is affected by the degree of spread of cancer). Surgery is usually reserved for non-small cell cancer because small cell cancer is more aggressive and requires other treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The operation is not recommended even if the tumor affects the trachea, or has moved to other organs, or any other serious medical conditions are present. To get rid of cancer cells that could remain after the operation, radiotherapy or chemotherapy is performed.
Radiotherapy - This is a tumor irradiation procedure that kills or slows down the growth of cancer cells. Radiotherapy is a treatment for lung cancer that It is effective in both small cell and non-small cell types of cancer. Radiotherapy is carried out in the case when the tumor has moved to the lymph nodes or if the operation is impossible due to contraindications (in case of severe diseases of other organs). Often, in order to achieve greater effectiveness of treatment, radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy is a method of treating lung cancer, the essence of which is to take special drugs that kill cancer cells or stop their reproduction and growth. These are drugs such as Docetaxel (Taxotere), Bevacizumab (Avastin), Doxorubicin and the like. Chemotherapy is used to treat both types of lung cancer - small cell and non-small cell. Although chemotherapy is considered one of the treatments for lung cancer, it is not always possible to cure cancer with its help, but it can increase the life of a person, even in the case of an advanced stage of the disease.







